Air craft technique is one of the geo-engineering methods to reduce global warming. This method was the most cost effective, and yielded the largest benefits. It could also be conducted covertly to avoid the burdens of environmental protection and regulatory entanglements.Under the air craft techniques, we have Solar radiation management (SRM) technique. This technique reflects Sunlight away from the Earth by hazing the sky with aerosols such as sulfur dioxide or aluminum oxide.
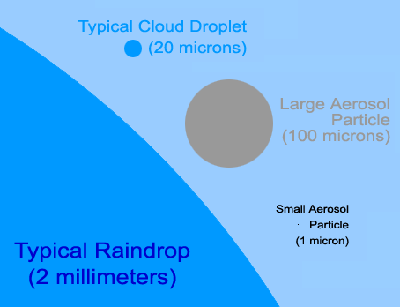
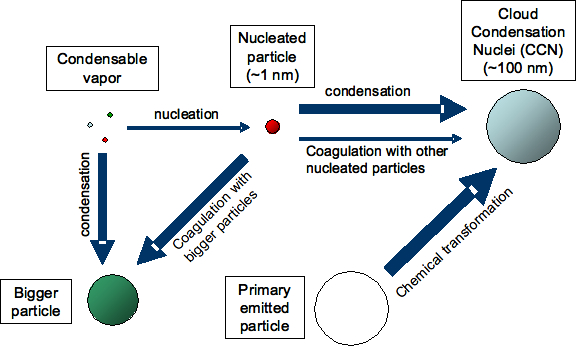
an air craft injecting aerosol in the atmosphere Artificial modification of Earth's climate systems using reflective nano-materials (aerosols) to reflect sunlight. Aerosols are very fine suspensions of solid and liquid particles in gaseous form that range in size from 0.1 to 1 micrometer (µm) in diameter. These aerosols normally persist in the lower stratosphere (the second highest layer of the atmosphere) at small background concentrations. comparable size of nano materials ( aerosol) with cloud droplet and raindrop The aerosols are dispersed via jet aircraft trails that expand into reflective artificial clouds. Fleets of small jet aircraft could fly into the lower stratosphere several times a day and release sulfur gas to produce planet-cooling sulfate aerosols. Aerosols exert their cooling effect through two mechanisms: the aerosol "direct effect," and the aerosol "indirect effect." They act primarily by reflecting solar radiation back into space (the “aerosol direct effect”), thus increasing the planet’s albedo and lowering temperature levels. They can also act as cloud condensation nuclei (CCNs), providing scaffolding around which cloud droplets can coalesce and form clouds (the “aerosol indirect effect”). The higher the number of particles, the more reflective the clouds tend to be. Recent analysis suggests that the effectiveness of stratospheric aerosol climate engineering through emission of non-condensable vapors such as SO2 is limited because the slow conversion to H2SO4 tends to produce aerosol particles that are too large; SO2 injection may be so inefficient that it is difficult to counteract the radiative forcing due to a CO2 doubling. Here is an alternate method in which aerosol is formed rapidly in the plume following injection of H2SO4, a condensable vapor, from an aircraft. This method gives better control of particle size and can produce larger radiative forcing with lower sulfur loadings than SO2injection. Relative to SO2 injection, it may reduce some of the adverse effects of geoengineering such as radiative heating of the lower stratosphere. This method does not, however, alter the fact that such a geoengineered radiative forcing can, at best, only partially compensate for the climate changes produced by CO2. SRM SIDE EFFECT: |
- · Reduces direct sunlight which is vital to fundamental life processes such as photosynthesis.
- · Lessens the public will to address climate change with low-tech common sense solutions.
- · Compromises physical and mental health (vitamin D deficiency, depression, asthma).
- · Causes continued ocean acidification from CO2.
- · Further depletes ozone.
- · Increases dangerous ultraviolet radiation.
- · Increases diffuse radiation, making the sky less blue and diffuse radiation, decreasing solar power production.
- · Risks potential for military use.
- · Affects local and global weather systems.
- · Risks much more rapid global warming, if discontinued.
- · Puts permanent pollution above astronomers’ telescopes.
- · Assures there will be human error with sophisticated technical systems and unexpected consequences.
- · Tarnishing of the sky: Aerosols will noticeably affect the appearance of the sky, resulting a potential “whitening” effect, and altered sunsets.